5G is one of the buzzwords that is currently prevailing in the smartphone world not just in India but across the entire Globe.
What is all this hype about 5G? Why would it benefit us, the end-users? What are its advantages? Is there any special hardware required to avail of the 5G services? We will try our best to clear all your doubts and questions on the 5G cellular network in this short yet concise article.
History
Comparing to some other countries, India is relatively slow in adapting to newer and modern telecommunications standards as we have seen with the 4G rollout.
We were late to the party while our small neighbours such as Bhutan and Bangladesh had already upgraded most of their networks to 4G LTE.
Even now, our government-owned carrier BSNL is yet to completely roll out 4G in India.
While the average 4G download and upload speeds across the world is somewhere around 35Mbps and 12Mbps respectively, in India it is just 12Mbps and 4Mbps. The quality of 4G service, even though one of the cheapest in the world is pathetic, to be honest.
In such a scenario, we hope that rolling out 5G networks in the future will improve the situation significantly. India is a big country with 1.3 billion people, most of whom are using or going to be using smartphones and a cellular network without bottlenecks and congestion is of utmost importance.
Timeline of mobile network evolution
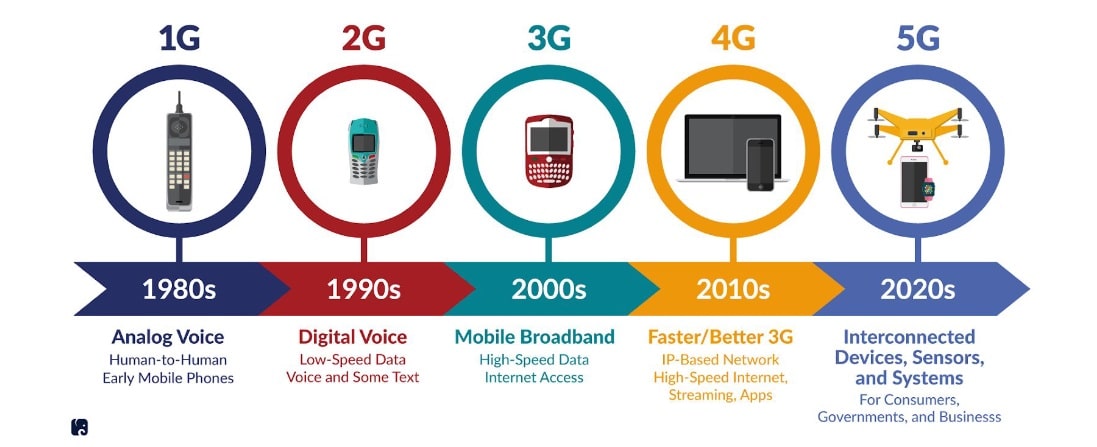
What is 5G?
5G is the newest global cellular wireless network standard which succeeds the 4G with the added advantage of wider bandwidth of seamless connectivity, increased capacity and wider availability.
5G works similar to its predecessor in a cell to cell communication manner. The service area under a particular tower is designated as a cell. All the devices that fall under a specific cell are connected to the internet and voice network by a transmission tower within the cell utilizing radio waves.
Types of 5G spectrum
There are three types of proposed 5G network types, each of which varies from one another in terms of frequency, speed and range.

Low Band 5G
Low band 5G is almost similar to the existing 4G cellular network in terms of signal coverage. This particular 5G band operates in the 600-850MHz spectrum and offers speeds up to 250Mbps.
The low band 5G network is supposed to be at least twice as faster as the existing 4G LTE network in terms of internet speeds.
Low band 5G is considered to be the baseline form of a 5G network that will be readily accessible to anyone with a 5G ready smartphone in hand.
Mid-Band 5G
Mid band 5G network consists of microwave radio signals ranging from 2.5-3.7GHz, capable of providing internet speeds up to 900Mbps and almost 4% faster when compared to a baseline low band 5G network.
The network coverage of the mid-band 5G extends up to a few kilometres from the transmitting tower. Such a 5G network is ideal for small towns with a sizable population but not as concentrated as that of a proper city.
High Band 5G
High band 5G is also termed mmWave 5G which is the top tier 5G network that operates within a frequency range of 25-39GHz. This 5G network will deliver gigabit speeds to the customers with compatible equipment but the operating range is limited.
A mmWave 5G network needs multiple cells with transmitting towers for covering a smaller section, thereby significantly increasing the operation and infrastructure setup and maintenance costs.
Device availability
Even though the 5G network is still in its initial testing stages in India, this has not stopped the companies from rolling out 5G enabled smartphones.
All popular smartphone brands are aggressively pushing 5G readiness in their device marketing ads and posters.
You can get hold of a 5G capable smartphone for as low as Rs.16,999 in the Indian market at present. There are multiple affordable models available from brands such as Realme, Motorola and Xiaomi – all of them with the support for baseline low band 5G support.
Do note that budget 5G smartphones won’t come with the support of all types of 5G bands which we discussed in this article. So keep an eye for the band support on each smartphone before you make your purchase decision. Most of the premium flagship smartphones, however, come with support for most of the 5G bands used worldwide.
Advantages of 5G
- Significantly better data transmission speeds
- Lower latency
- Increased network capacity
Disadvantages of 5G
- Requires 5G capable devices; not backward compatible with 4G devices
- Higher infrastructure setup costs
- Quality of service with vary depending on device capability
Applications of 5G
First and foremost 5G as we said enables high-speed wireless data transmission via cellular-enabled devices such as smartphones and tablets.
This high speed, congestion-free, low-latency 5G network can be utilized for several purposes such as telemedicine, IoT management, industrial automation etc. and much more.
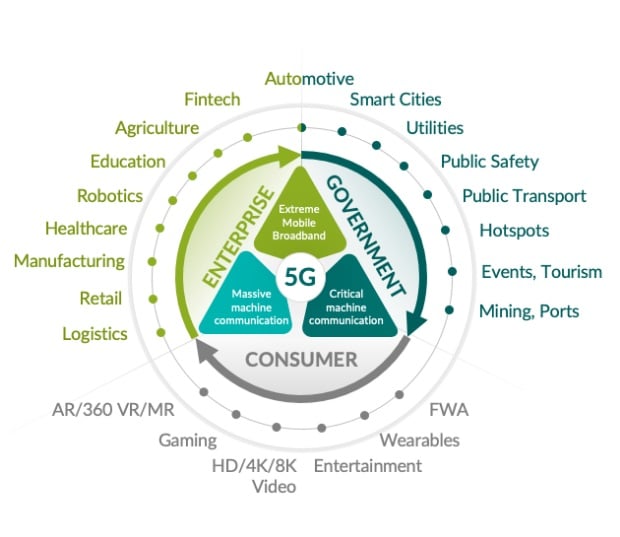
Since a robust 5G network alleviates most of the downsides of a typical 4G or Wi-Fi such as network congestion issues, range and data speeds, it can be considered as a total network solutions replacement for such purposes.
As the development of the 5G network is still a work in progress, we are not completely aware of most of its future use cases, but for sure it will indeed be a significant upgrade from today’s cellular network standards and performance.
Security concerns
Recently amidst the global fear of industrial espionage by certain Chinese OEMs, India has decided to source 5G equipment either from homegrown industries or from non-China vendors such as Ericsson, Siemens, Nokia and Samsung.
While no official decision has been yet taken, in theory, OEMs such as Huawei and ZTE are excluded from participating in the 5G trials.
To ensure a more secure network regime, the Indian government has earlier proposed to procure 5G equipment from trusted sources, which the people familiar with the industry strongly believe is a clear message to exclude China-based vendors from the 5G equation in the country.
Conclusion
While the 5G testing in India is yet in its infancy with trials set to begin sooner or later, we hope the rollout will be quick and uniform across the country from all operators.
We expect 5G to close the wide gap between the rest of the world and India – that is the abysmal cellular network performance that we have seen with the 4G networks here.
With this, we are winding up this short blog about 5G cellular networks. If you have any questions regarding this article, let us know in the comments section below. Thanks for taking the time to visit and read our content. Have a nice day!


