While scouting the internet to purchase a smartphone, you may have noticed these terms used in display specification; OLED, AMOLED, Super AMOLED, Fluid AMOLED, LCD, or IPS LCD.
What are these?
And how they can affect your user experience is what we are trying to address here.
Many people trade the display just for the sake of good battery life but the display is the most superficial component that we use to interact with the smartphone. Ignoring it can be a real waste of your hard-earned money.
Today, we will give you an in-depth explanation of AMOLED vs LCD which are the two commonly found display types on a typical modern smartphone.
AMOLED
What is an AMOLED? The full form of AMOLED is an active-matrix organic light-emitting diode, and it is a type of OLED display.
In OLED displays, individual pixels integrated onto a thin film transistor (TFT) array light up when the power is supplied.
The current supplied to these pixels are controlled by two TFT’s.
- The first TFT starts and stops the charging of the storage capacitor.
- The second TFT provides a constant power supply to each pixel to light them up.
To understand the above points in simpler terms – when you lock your smartphone every pixel will be turned off and the screen will look completely black and as soon as you unlock your device and start using it, only the necessary pixels will lighten up.
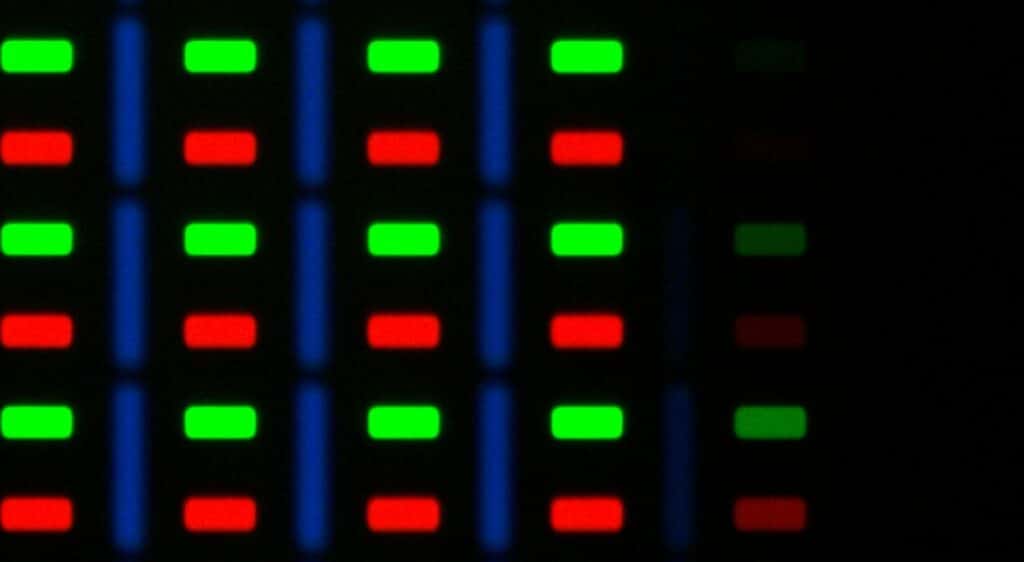

One major advantage of the AMOLED panels is that only those pixels which are required will light up and the rest of them will remain turned off.
This technology offers the panel to have a theoretically infinite contrast ratio, leading to inky deep blacks and vivid and punchier colours on screen. Also, because not all pixels light up on the screen, AMOLED screens are slightly more battery efficient than LCDs.
LCD
Liquid crystal display (LCD) is one of the most common display types that is found on the majority of our consumer electronics products including televisions, laptops and smartphones.
LCD technology employs light modulating properties of the liquid crystals combined with polarized filters.
The LCD panel does not produce light by itself; it requires a backlight or reflector to produce colours in images.
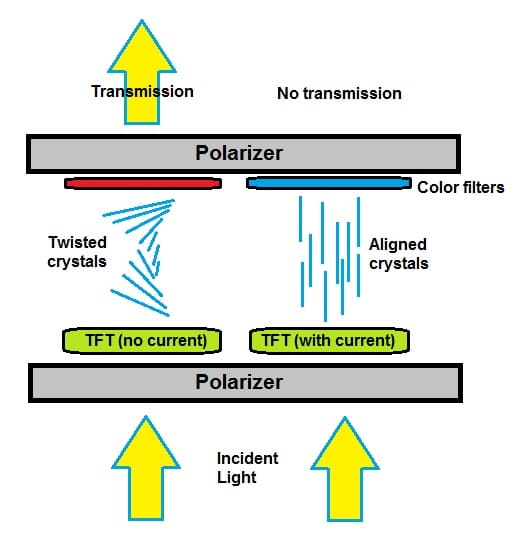
The polarized filters at the start and end both have vertical and horizontal cuts respectively.
Liquid crystals are the central element in the process that controls the amount of colour and the light that passes through them.
By controlling these molecule’s arrangement, an image in light can be controlled or manipulated. Unlike the AMOLED panel, the LCD panel has only a single source of light.
Difference between AMOLED and LCD
The major difference between the AMOLED and LCD is the light source. Each pixel of an AMOLED display has its light source whereas the LED panel has only a single light source.
AMOLED panels are characterized by rich pixel density therefore the image looks sharp and clear and talking about the LCD, it has less pixel per inch.
The power consumption in AMOLED panels is less compared to LCD. Like we said earlier in the blog post that in an AMOLED panel, pixels are only being used when necessary and LCD panels consume the same amount of power all the time while in use because it will light up all the pixels simultaneously.
LCD panel production is much cheaper than AMOLED display and even if it breaks, the procedure of replacing it is easy and is cost-effective. Also, the whites in the LED are much brighter when compared to AMOLED.
After reading the above statement you now know that AMOLED is very expensive and can be only found in premium or mid-range smartphones.
The problem in LCD is with the blacks – even if the display is not in use the black does not look like deep black instead it is more like a grey colour and this is not the case with OLED panels.
The AMOLED panel has much more legible visuals than the LCD but when we speak for the brightness, the LCD stays on top as it is brighter and even under direct sunlight you can use the panel effortlessly.
The LCD panels are slightly thicker compared to the AMOLED and one of the downsides of AMOLED is they are thin and if any individual LED gets damaged you notice colour bleeding issues on the screen and trust us the replacement cost is expensive.
The AMOLED panel life span is less compared to the LED, but don’t worry, even if you purchase a smartphone with an OLED display it will last for about 2-3 years without any issues.
Now comes the main point – colour reproduction.
The AMOLED panel exhibits warm colours, a rich contrast ratio and better viewing angles that give a pleasant experience to the user while the LCD panels offer a decent colour reproduction.
The fact is LCD panels are of different varieties and over the period it has improved a lot. The IPS LCD is the best LCD that has natural colour reproduction and better viewing angles.
Advantages of AMOLED panel
- Power-efficient
- Better colour reproduction with rich contrast ratio
- Excellent inky deep blacks
Disadvantages of AMOLED panel
- Manufacturing and replacement cost is high
- Colour bleeding issue if any individual pixel fails
- Sunlight legibility is slightly lesser than in an LCD
Advantages of the LCD panel
- Easy manufacturing with less cost
- Excellent display brightness
- Compact and thin
- Decent colour reproduction
Disadvantages of the LCD panel
- Power consumption is high
- Only a single light source
- The blacks are not perfectly black
Price and Usability
We have explained the technical jargon in simple terms but everyone has a different budget and way of using their smartphone so choosing the right type of display will vary from user to user.
Pricing of AMOLED vs LCD panel:
You can find smartphones sporting AMOLED panels starting from Rs.12,000 and higher in the current Indian market.
However, the quality of the AMOLED panel used might vary significantly between budget smartphones and premium flagship models.
The companies use marketing terms like Super AMOLED, Dynamic AMOLED, or Fluid AMOLED but in the end, these all are the AMOLED panels; the only difference is brightness level, pixel density, refresh rate and contrast ratio.
Speaking of smartphones with LCD panels, it can be said that most entry-level, budget and even mid-range smartphones come loaded with LCD.
LCD is also available in multiple types like IPS LCD, TFT LCD, and PLS LCD, and more alike. The IPS LCD is one of the most commonly known superior LCD types as it has good colours and brightness with excellent viewing angles.
Usability – Which is the best panel for your smartphone?
Let’s begin with the question, who should buy a smartphone with an AMOLED display?
If you love watching media content or having a vivid display is what you’re after then you should buy a smartphone with an AMOLED panel.
The AMOLED panel should not be a big concern to mobile gamers as in gaming what’s more important is the higher refresh rate and touch sampling rate.
The IPS panel should be your priority if you like natural colours instead of saturated punchy colours. This display is for those who just use their smartphone regularly like for gaming, calling, messaging, and social media.
As the display technology is improving day by day, many IPS LCD panels now come with a 120Hz refresh rate which is amazing as you get a buttery smooth experience in gaming as well as in regular use.
Conclusion
Both the panels have their advantages and disadvantages and it all boils down to your preference and the budget.
If you hold the budget around Rs.15,000 then having a smartphone with an IPS panel is completely fine but if you have more like Rs.20,000 or above then going for an AMOLED panel is a better option.
We at bettershark prefer AMOLED display, to be specific Samsung’s Super AMOLED as it gives much pleasant experience, not just in terms of colours but the panel are bright and touch responsive as well.
That’s it, we hope you understand the difference between AMOLED and LCD panels in detail. We have tried to explain technical details in simple terms.
Still, if there is anything you have in mind do let us know in the comment section. As always, thanks for your time and have a nice day!
