Smartphones these days come with bigger and beefier batteries to sustain a long usage even with all the high-end hardware and software features its packed with.
As time being the most precious currency for humans, those who wait for their smartphone batteries to fall under 10% charge it up again are almost a tale from the past.
We hate waiting for our phone to get juiced up right?
People tend to charge their smartphones more often during the breaks when they keep their hands off the phone. And here comes the importance of fast charging.
Fast charging significantly reduces the charge times. Different companies have introduced their own versions of fast charging technology, which we would like to explain to you in this article.
Without further ado, lets dig in deep to find more exciting information on this relatively obscure topic that often gets unnoticed when making a smartphone purchasing decision.
How does a battery work?
Starting from the basics of a battery will certainly give a strong foundation about how the charging technology works.
A battery consists of an anode (negative terminal), a cathode (positive terminal), and an electrolyte.
Electrolyte serves as a catalyst for better conductivity of ions within the battery.
When the circuit is complete, chemical reactions occur inside the battery and electrons will start forming in the anode.
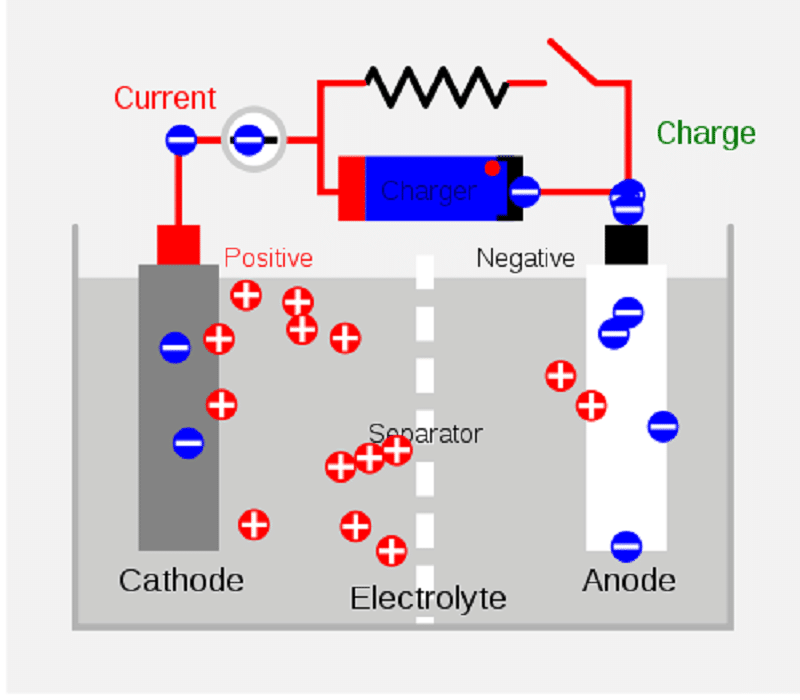
This electron buildup in the anode causes a potential difference as the cathode has fewer electrons than the anode.
In Order to achieve stability, electrons from the anode transfer up to the cathode till uniformity is formed.
When the number of electrons around the cathode and anode reaches equal, the anode will stop supplying electrons and thus the power delivery stops.
When the battery is charged again, the anode and cathode are restored to original state.
Batteries in mobile phones
The batteries inside our mobile phones works based on the same principle stated as above.
Electrolytes in mobile phone batteries can be in solid, semi-solid or molten solid states.

Initially, Nickel-Cadmium batteries were used inside the cell phones but later replaced with Lithium-Polymer batteries which deliver better performance and efficiency.
Advantages of Li-ion batteries
Li-ion batteries don’t exhibit memory effect. In fact partial charging and discharging increases the lifespan of a Li-ion battery.
Nickel-Cadmium batteries exhibits a peculiar property known as memory effect.
These batteries had to be discharged to the absolute minimum before charging up again.
Constant partial charging will decrease the total charging capacity of these batteries, which is not at all advisable in resource critical use cases such as mobile phones.
Li-ion batteries are much more environment friendly than other forms of battery technologies.
Can be made lightweight and compact considering the amount of charge capacity they can carry.
Disadvantages of Li-ion batteries
Safety is the single most concern about using Li-ion batteries with smartphones.
These batteries are bound to quickly catch fire and explode, providing an internal malfunction or short circuit. Extra care has to be implemented to prevent this from happening, which adds to the R&D costs.
Common smartphone fast charging technologies
Many brands design and develops their own implementations of fast charging technologies.
There a handful of such popular methods currently used in smartphones around the globe.
In this section, we’ll take a look at some of them to understand the technology in a bit more detail.
Qualcomm Quickcharge 4+
Qualcomm is a major mobile SoC manufacturer, holding about 38% of smartphone SoC market revenue share.
The Quickcharge 4+ is the homebrewed fast charging solution from Qualcomm that succeeds the Quickcharge 4.

Quickcharge 4+ was first implemented with Snapdragon 835 processor. This SoC, when compared with the predecessor Snapdragon 821, was about 25% more energy efficient.
Qualcomm claims that the Quickcharge 4+ can theoretically charge an empty battery to 50% in 15 minutes.
This technology works on the basis of consistently supplying high voltage to the device which requires charging.
By the equation Power(W) = Voltage(V) x Current(A), QC 4+ can deliver a power up to 18W for charging the battery inside your smartphones.
For eg., A Qualcomm Quickcharge 4+ certified charger with 9V and 2A amperage can output a power of (P = V * I = 9V x 2A) 18W to the device.
While the Quickcharge 3,2 and 1 was compatible with micro USB standards, Quickcharge 4+ is exclusively compatible with USB type C and supports USB – PD which we will detail in the coming sections.
Dual IC power management
Doubling the number of power IC’s for monitoring the power supply allows the device to have lower thermal dissipation (heat) and reduces the charging time.
Intelligent thermal balancing
The QC4+ technology automatically analyses the presence of any hotspots in the charging circuits and if detected, adjusts the voltage and current accordingly to ensure that there is no damage to the internal hardware.
This thermal balancing also avoids any CPU and GPU throttling which might occur when you plug in the device to charge and continue to use it.
Short circuit detection and avoidance
The power management chips constantly monitors the power and the temperature, and if anything abnormal is detected, stops charging the device.
MediaTek Pump Express 4.0
MediaTek Pump Express 4.0 is a USB-C PD (Power Delivery) based quick charge technology developed by the SoC manufacturer MediaTek for Helio series processors.
Featured in smartphones with Helio processors such the P60 SoC, MediaTek claims that this fast charging technology is twice as fast as the conventional smartphone charging times.

Pump Express 4.0 can deliver a maximum power of up to 25W with maximum voltage and amperage hovering somewhere around 5V and 5A respectively.
The company claims Pump Express 4.0 certified devices can be charged up to 75% in under 30 minutes.
USB – C PD (Power Delivery)
USB-C PD was standardized by the USB Implementers Forum (USB – IF) for power transfers across devices.
USB-C PD is capable of delivering up to 100W power for purposes ranging from smartphone charging to hooking up an independent 4K monitor.
Usually, USB-C PD protocol supplies power ranging between 7.5W to 28W when it comes to smartphone charging and over 28W when the connected device is a laptop or some other resource hungry gadget.
QC 4+ is compatible with USB-C PD. If a device with QC 4+ doesn’t have a QC 4+ charger around, it will get charged via USB-C PD standard pretty much faster.
Google supports USB-C PD over other proprietary fast charging methods. Apple devices too rely on USB-C PD for charging purposes.
Super VOOC by Oppo
Super VOOC is a proprietary charging standard from Oppo, a Chinese smartphone company.
This technology succeeds the VOOC fast charging technology.
VOOC stands for Voltage Open Loop Multi-step Constant-Current Charging and this technology at present is the quickest fast charging solutions out there in the smartphone market.

Super VOOC fast charging was first implemented in the Oppo Find X smartphone which charged from 0 to 100% within 35 minutes.
In Find X, the 3400mAh battery inside is split into two 1700mAh cells. These independent cells are charged with 10V/5A supply equating to 50W of power delivery.
Since the circuitry and all the necessary hardware for power control is located inside the charger, there is no heating issues within the smartphone hardware which might throttle the charging speeds.
Super VOOC charging technology, unlike the Qualcomm Quickcharge 4+, works on the basis of increased amperage supply.
Dash/Warp Charging by OnePlus
In reality, the Dash/Warp charging on the OnePlus smartphones is the Super VOOC technology licensed from Oppo, since they both are subsidiaries of a single company, BBK electronics.
OnePlus had recently renamed the Dash charging technology to warp charge due to copyright claims for the “dash” name.

The first smartphone from OnePlus to have released with this moniker is the OnePlus 6T McLaren edition.
The Warp charge technology has a maximum power output of 30W and the charger is rated at 5V/6A.
It takes about 20 minutes for a OnePlus phone with warp charging enabled to charge 50% and from 5% to 100% in just under 60 minutes.
Huawei Supercharge
Huawei Supercharge is the companies take on the fast charging master race.
This technology comes with a maximum power delivery capacity of 40W when the battery is juiced up with the supplied charger with a rating of 10V/4A.
Supercharge technology, which is in the market with phones such as the Huawei Mate 20 Pro can charge its battery from 0 to 90% in under 30 minutes.
Adaptive Fast Charging by Samsung
Adaptive Fast charging is just a rebranded Quickcharge 2.0 licensed from Qualcomm.
Adaptive fast charging technology delivers a maximum power of 15W and the chargers are rated for 9V/1.67A output.
Adaptive fast charging is one of the slowest fast charging implementations currently available in the smartphone market.
| Technology | Max Voltage | Max Amperage | Max Power | Time to charge |
| Super VOOC by OPPO | 10V | 5A | 50W | 0-100% in 35 mins |
| Huawei Supercharge | 10V | 4A | 40W | 0-90% in 30 mins |
| OnePlus Warp charge | 5V | 6A | 30W | 5-100% in 60 mins |
| MediaTek Pump Express | 5V | 5A | 25W | 0-75% in 30 mins |
| USB Type C | 5V | 4A | 20W | 0-75% in 45 mins |
| Qualcomm QC 4+ | 9V | 2A | 18W | 0-50% in 15 mins |
| Adaptive Fast charging | 9V | 1.67A | 15W | 0-50% in 25 mins |
Table 3.1 Charging speed compared between various standards
Wireless charging
Wireless charging is not essentially a fast charging process but definitely an interesting technology worth knowing about.
Many glass backed phones such as iPhone XS Max comes equipped with wireless charging capabilities.

Wireless charging works on the principle of magnetic induction.
Instead of a regular cable plugged in to the charging port on the phone, the charge is electromagnetically transferred between the wireless charging plate to the battery inside the smartphone.
The main advantage of this technology is that it is a completely wireless operation when it comes to the phone part.
Even though the induction base plate needs to be connected with the power source, just placing your wireless charging enabled phone on the plate will do the trick.
The major disadvantage of this technology is that the charging is not as fast as a wired charger. Also, the technology is expensive and require a seperate wireless charging station for the same.
Final words
Everybody likes to save time. Fast charging enabled smartphones to tap this emotional benefit from the customers, making it a very desirable quality worth looking for while purchasing a smartphone.
The fast charging technology has just begun to flex its muscles and has a lot of room for improvement in the future.
The battery is the single most weak point in the smartphone, which is bound to see a lot of innovations in the coming days both in terms of increased capacities and form factor.
It is almost sure that, along with the innovations regarding batteries, charging technologies too will improve over time.
Talking about innovations, we have much more articles lined up for you on this site that explains to you about the technologies surrounding gadgets in the simplest possible manner.
Be sure to read them and if you liked it, don’t forget to subscribe to our weekly newsletter for more updated tech contents and buying guides right inside your inbox.
Thanks and have a fruitful day ahead!
