The Internet has come a long way since its first precursor format – the ARPANET, developed by the US defence department for connecting computers in their internal networks. Now the internet is one thing that most of us can’t live without – our work, social life, hobbies – everything we do has something or the other to do with the internet or its related services.
Especially since the start of the Covid pandemic, we are more reliant on the internet than ever before and we thought it’s a good time to write an article about the FTTH (Fiber to the Home) technology which is one of the emerging technologies that provides most of us with the internet, here in India.
We sincerely hope that this article will provide you with a rough idea of what makes the FTTH technology work much better than its predecessors and help you choose your ISP accordingly. Without any further ado, let’s begin!
Broadband Internet
Broadband in general is a wide communication band that supports simultaneous signal transmission at once via different connecting mediums such as coaxial cable, twisted-pair copper cable, optical fiber cable etc and can even be completely wireless.
High-speed broadband came as a successor to the low speed, less efficient analog dial-up internet which some of us might remember back in the day came with your landline connection.
Even though there are different types of broadband available such as DSL, cable modem, satellite etc, we are focusing on the newer and most popular FTTH which uses optical fiber cables to transmit data at higher speeds and with minimal signal loss.
Fiber To The Home
FTTH technology leverages optical fiber for signal transmission in the form of light rather than the electrical signals in the case of a DSL internet connection.
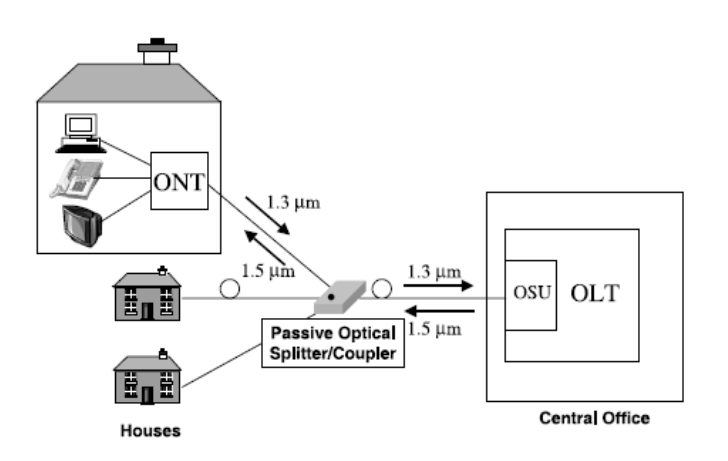
An FTTH connection involves connecting a central signal distribution node with an individual living space (home) via optical fiber cable which then terminates in an ONT/ONU (Optical Network Terminal/Unit) which is one of the CPE (Customer Premise Equipment).
This ONT/ONU is then connected to an internet router which then delivers signals for us to use the internet via a wired LAN connection or Wi-Fi.
Passive Optical Network (PON)
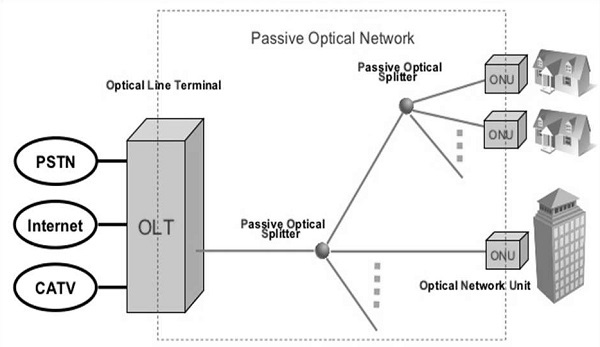
Passive Optical Network is a point to multipoint network system where the signal from the distribution side is shared with several individual users by using passive components such as optical splitters along the transmission line.
There are commonly two types of PON – EPON and GPON.
While we are not delving into this deep, EPON is cost-effective, easy to scale PON whereas GPON offers superior performance and data security but at the expense of increased operating costs. Most ISPs in India, at least in states such as Kerala, rely on expensive GPON systems.
The maximum distance that a PON network can deliver its service is around 20km.
Components of an FTTH network
The FTTH network consists of different components along the fiber line that helps to transmit, channel, receive and broadcast data from the main service provider to the end-user.
In this section, we will discuss some of the most important network components in an FTTH network.
Optical Link Terminal (OLT)
OLT is a piece of networking equipment that is directly connected to the internet superhighway through which it receives internet signals to re-transmit to the customers.
OLT is a Provider Premise Equipment (PPE) with several ports to receive signals from multiple ISP’s and output ports to transmit these signals along the fiber line.
The OLT does not only transmit signals to the user side but also receives the data that is sent from the user side, thereby enabling two-way network communication.
Optical Network Unit/Terminal (ONU/ONT)
The ONU/ONT is a Customer Premise Equipment (ONU/ONT) where the transmission cable from the OLT terminates after passing through multiple optical splitters.
There is very little difference between ONU and ONT, but both share the same purpose of receiving data from the OLT and optimizing and sending the data back from the customer to the OLT.
Optical Distribution Network (ODN)
ODN is one of the most important components of a PON system.
It is the physical media through which the OLT on the provider premise and the ONU/OLT on the customer premise is connected.
As we mentioned earlier, a typical PON system can serve a maximum area of up to 20km from the OLT.
The ODN is the primary variable within a PON system that determines the quality of the signals and is directly responsible for the performance and reliability of the system.
Advantages of Fiber To The Home connection
FTTH brings many significant advantages along with it when compared to the DSL internet, some of which are listed below:
Wide bandwidth
Optical fibers which are used for signal transmission in the FTTH system can carry almost 10x more data than a conventional copper cable. This is very important because the internet data usage is increasing exponentially as we speak and the extra bandwidth helps in avoiding bottlenecks along the ODN (Optical Distribution Network).
Multiple users can enjoy faster internet services such as IPTV, VoIP etc simultaneously without any drop in performance.
Versatility
Optical fiber systems can carry data 400x further without incurring any signal losses and almost 10x faster. Copper cables used in DSL networks tend to significantly degrade the quality of signals after a few splits in the line, which might affect the end-user far away from the OLT (Optical Link Terminal).
However, with FTTH and optical fiber, you won’t have that issue. Light signals are not susceptible to interference from electrical signals and this ensures clean and high-quality signals from the provider to the end customer.
Easy Upgradation
Since the optic fiber used to transmit signals in an FTTH system is future proof, both the providers and the customers only need to upgrade their respective systems to scale up the existing network, enhance performance and add new services.
The ODN infrastructure can be kept intact and the services to the customers won’t be affected even if the provider decides to upgrade his equipment.
End users can also switch devices on their end such as internet routers for faster internet, better signal coverage and much more.
Major FTTH providers in India
Surprisingly India is one of the leading countries which implements the modern FTTH service rather than still relying on old DSL service like some other western countries.
There are several Class 1 ISPs such as Airtel, BSNL and Jio providing FTTH internet across the country and some secondary ISPs such as GTPL, Asianet, Kerala Vision providing similar internet services in different parts of the country.
BSNL Bharat Fiber
BSNL has been in the DSL internet business for a while and the Bharat Fiber is the exclusive FTTH service from BSNL in which they directly provide internet connectivity to those who live near the telephone exchange and via local cable operators (LCO) for others.
To compete with the rivals such as JIO and Airtel, BSNL has started offering attractive promotional plans with welcome offers such as Rs.449* plan for 30Mbps with a data cap of 3300GB per month. This plan is valid for six months from the connection date after which the users will be automatically migrated to the Rs.599* plan which gives speeds up to 60Mbps for up to 3300GB per month.
To know more about area-specific FTTH plans from BSNL, visit their tariff page here – BSNL Bharat Fiber plans.
Jio
Jio recently launched the Jio Fiber in select cities with affordable unlimited internet and a promotional offer that provides a free one month trial.
The FTTH plans from Jio start at Rs.399 for a 30Mbps plan with a monthly data cap of 3300GB. On higher tariff plans Jio bundles various OTT platforms as well. If you stream a lot of OTT content, it’s better to choose Jio if it’s available in your area.
One major downside of choosing Jio is that they provide a locked modem that can be customized in any way.
To know more about Jio Fiber plans, you can visit their tariff page here – Jio Fiber Plans.
Airtel
Unlike BSNL and Jio, Airtel broadband is only available in selected cities around the country. Airtel offers unlimited internet starting at 40Mbps speeds for Rs.499 per month.
Similar to Jio, Airtel also bundles various OTT and streaming services with its monthly internet packs.
To know more about Airtel broadband plans, you can visit their tariff page here – Airtel broadband Plans.
With major ISPs such as BSNL, Jio and Airtel, you will get unlimited free voice calls as well. You just need to buy a land phone and connect it with the FXS port on the modem to avail of this feature at no additional cost.
Internet Speeds – Mb/s Vs MB/s
Internet speeds you receive will vary significantly between ISPs and according to the monthly plan you have chosen.
ISPs usually denote their plan speeds in Mb/s or Mbps. Do note that this is megabits in computer terms and shouldn’t be confused with megabytes. Suppose if your ISP has given you an internet connection with a rated speed of 30Mbps, it means the average download speed you get will be around 3.75MB/s.

As a quick shortcut, dividing the speeds in Mbps by 8 will get you the actual download speed of MB/s.
If normal browsing and video streaming is your primary need, choosing a 30Mbps plan is more than necessary. However, if you have multiple members using the internet and all of them are heavy users, it is always better to go for a 50Mbps plan or more to ensure there will be no buffering in between while all of you might be simultaneously using the internet on devices such as laptops and smartphones.
Do home users need internet plans with 200Mbps or more? Honestly, no. Even if you are a hardcore internet user, anything more than 100Mbps won’t result in anything drastically different in terms of usability experience.
Gaming
Unlike earlier days, where we sat in the room in front of the computer playing games all by ourselves, modern games offer multiplayer modes in which you can play or compete with people all over the world right from your bedroom.
The gaming servers of such online games are hosted in different parts of the world catering to the players in that region. In highly competitive games such as PUBG and COD, each microsecond is important and a slight latency in connection with the game server will make or break the experience for you. That’s where the term “ping” comes into play.
Ping is defined as the time taken by the signal from your computer to reach a host and come back to your device. The more the ping, the higher is the latency and the lesser it is, the better.
In online gaming, having a low enough ping is very desirable. However due to bad routing, even if your ISP delivers the promised speeds, the ping might be on the higher side. It is always wise to check with your ISP or your friends to know more about this.
Triple Play Services
Triple Play services simply mean provisioning three services – internet, VoIP and TV services through a single FTTH connection.
Most of the major ISPs offer triple-play services at affordable rates so that you no longer need separate connections for phone or TV anymore.
This is possible because of the wide bandwidth of the FTTH system and is a relatively new service in India that is fast catching up.
Tips to diagnose your FTTH signal quality
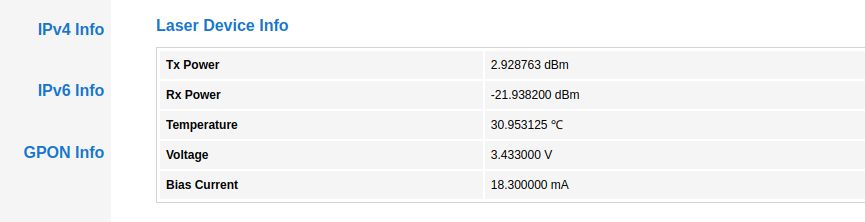
If you are an existing FTTH user and have the username and password for your CPE( customer premise equipment), you can easily check out the signal quality that you are receiving on your end from the service provider.
All you have to do is log in to the modem using the username/password and look for a tab or an option titled GPON Info. Do note that since the Jio modem is locked, you may not be able to access these settings.
Under the PON information tab, look for two values namely Rx and Tx power. Ideally, the Rx power should be between -15dBm to -24dBm and the Tx power should be somewhere between 2 to 3dBm.
If you are facing speed drops or network fluctuations often with your FTTH connection, do check these values and if they are not in between the specified range, it means there is some issue with the fiber splicing and should contact your service provider.
Conclusion
It is of assured guarantee that FTTH is the future of the internet and the optical fiber technology is indeed the perfect solution that can handle all our increased data consumption needs eliminating the bandwidth bottleneck and the signal loss issues that were inherent with the old DSL internet connections.
Value-added services such as VoIP and IPTV makes FTTH internet service an allround solution for productivity and entertainment at affordable rates.