We all have experienced switching the USB port back and forth at least twice before successfully plugging it into the device.
On a superficial level, USB C solves that very problem and much more than that which we will discuss in this article.
It’s been almost 2 year since the USB Type-C standard came out and yet the rate of adoption is really slow, especially among budget laptops and smartphones.
This article aims to detail about the USB Type-C technology, its working and the advantages it brings to the table. So without wasting any time, let’s get straight to the exciting stuff!
History
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is an industry standard set by prominent equipment manufacturers for establishing a connection between a host device and its supporting peripherals.
Initially introduced way back in 1996, the USB protocol is maintained by the USB-IF (Universal Serial Bus – Implementers Forum), which is a statutory body for overseeing the developments in the USB field from time to time.

USB charging cable
This protocol was implemented by the forum for easy and seamless integration between peripheral devices manufactured by different companies and the host devices.
This uniformity in connectivity improves the user experience and versatility for a range of devices. The initial version had a paltry data transfer speed of 1.5 Megabits per second (Mbps).
The second iteration of the original USB 1 was made in 2001 named USB 2.0 with improved data transfer speeds. The maximum transfer speed here was 480 Mbps.
Then again, after a gap of 10 years, USB 3.0 came in to existence which theoretically offered 10 times the speed and efficiency of existing USB 2.0 implementations. It had a maximum transfer speed of 5 Gigabits per second (Gbps).
The USB 3.1 protocol is the latest and greatest USB standard which is still in its infancy and being widely adopted among various OEMs around the globe. Theoretically it has a maximum data transfer speed of 10 Gbps.
USB Type-C
USB Type-C is the latest industry standard connector for transmitting data and power across two devices or between a device and a peripheral unit.
USB Type C differs significantly in size and shape with its predecessors. The Type-C port is much smaller, thinner and is twice as fast as a USB 3.0 protocol with speeds up to 10 Gbps.
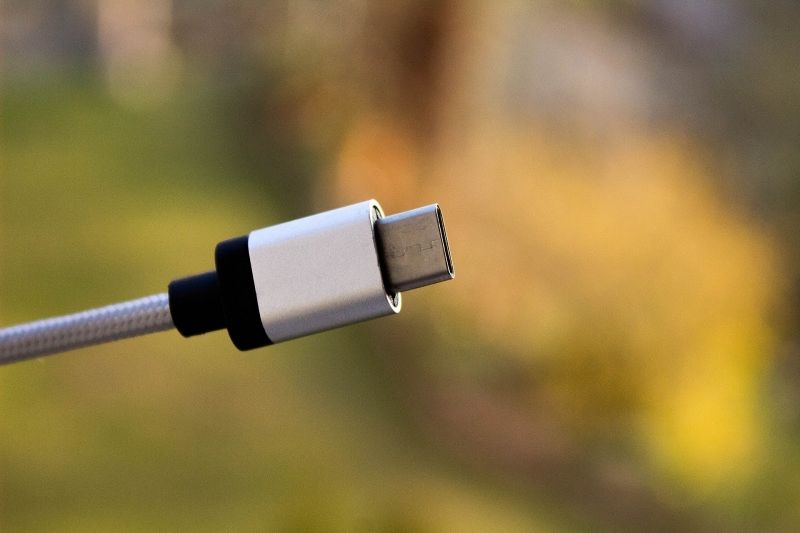

There is no up and down orientation for a USB Type-C cable and it can be plugged in to the port successfully in the first try itself thanks to the reversibility of the connector.
USB types, like A, B, and C, denote the shape and form-factor of the port and connector, rather than the data transfer speed. Many modern devices have moved away from the classic USB-A, USB-B, and micro USB ports to USB-C which is small, reversible, and has higher data transfer speeds.
It is to be noted that the USB C is the type of the connector and the USB 3.1 is the standard connectivity protocol mostly followed by the connector.
Physical Layout of a USB Type-C Connector
The USB Type-C connector consists of 24 pins. When compared with the predecessor USB 3.0 Type B connector having just 5 pins, this is a significant spec bump in the right direction.
In simple words, more the number of pins, better will be the data and power transfer capabilities
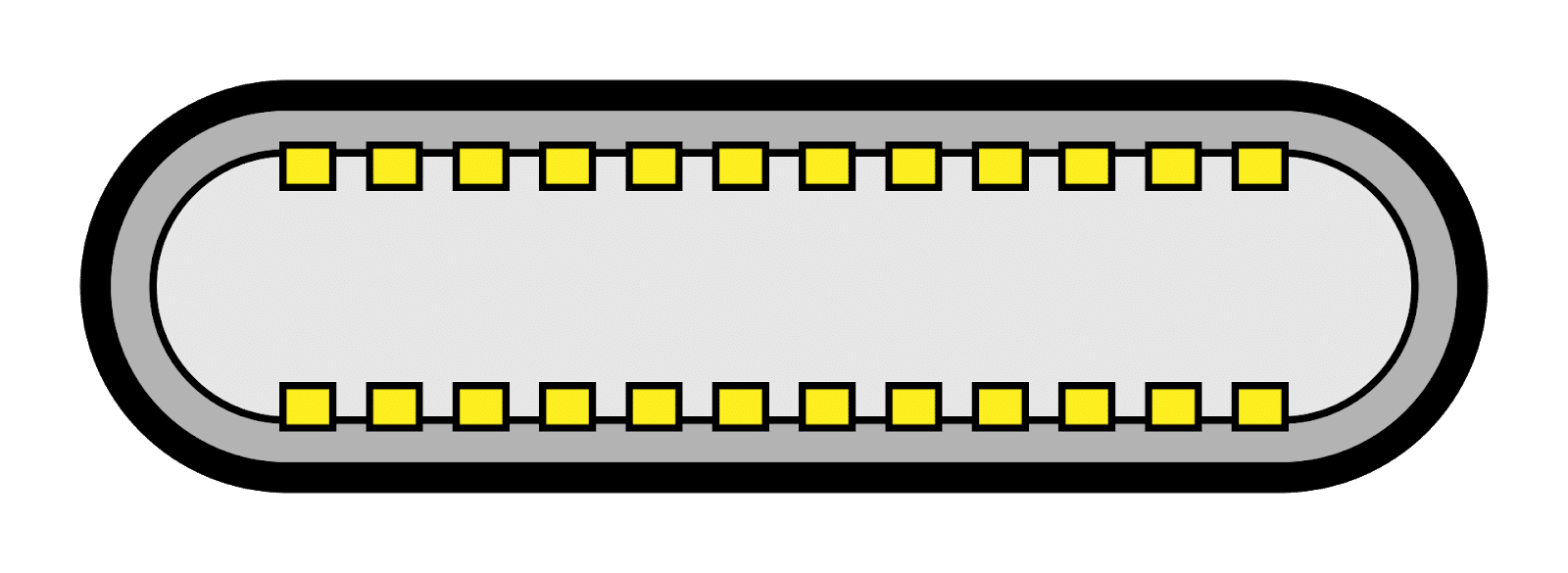
The physical size of a typical USB Type-C connector is 8.44mm by 2.6mm. The connector itself is called the plug and the host port is termed as the receptacle. The plug goes into the receptacle to complete the circuit.
There are two sets of wires on a USB 3.1 Type-C connector. One set for power delivery and the other set for data transfer.
This dual channel arrangement aides in much better data transfer speeds between the host device and the recipient device.
Compatibility with the Older Hardware
The USB Type-C connector in itself is not physically compatible with the older USB standards, the reason being that the size and form factor is entirely different.
The USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 was compatible with each other physically because both had the same form factor.
However, the underlying USB 3.1 protocol is reverse compatible with older devices.
You can use a suitable adapter to connect a USB C device with older hardware for all regular purposes, albeit with reduced data transfer and charging speeds.
Cable Identifier Chip
USB C cable might be an elegant piece of peripheral that looks compact and cute, but it also comes packed with neat little tricks to enhance the usability.
It’s known that many of the chipsets currently on our smartphones support features like fast charging, but somehow the cables we use doesn’t allow it.
The USB C connector comes with chips inside named electronic markers which informs the phone or laptop that the cable is capable of carrying increased current capacity. This allows the device to be charged in its full potential.
However, there are certain OEMs who prefer not to activate the fast charging even if the chipset used in the device supports the function.
This marker chip also provides information about the type, vendor, maximum current carrying capacity which makes the host to recipient connectivity safe and secure.
Manufacturers can even limit the device not to function with dubious third party cables from the market which might harm your device.
Charging and Data Transfer Statistics
A USB Type-C cable carries a minimum of 3A and can go up to 5A with compatible devices.
USB C to USB C cables must have a marker chip inside them to specify this current carrying capacity.
Most of the USB connectors support dual role data mode, where they can support USB on the go mode (OTG) for connecting peripherals directly to gadgets such as smartphones.
The connector also supports audio output mode, which acts the same way as a 3.5mm jack.
The only difference is that the earphone or headphone you are using must be compatible with the connector or there should be a USB C to 3.5mm adapter.
Thunderbolt Port
Thunderbolt port is a hardware interface developed by Intel in collaboration with Apple.
Thunderbolt port is used to connect external peripherals to a computer or a laptop and works similarly as USB Type-C for the most part.
The Thunderbolt port is a relatively newer technology, first introduced on commercial devices in 2011.
The earlier two versions of Thunderbolt used the same connector form factor of then standard MDP (Mini Display Port), which was large and bulky.
With the Thunderbolt 3, the connector has the same form factor as that of a USB C connector, which is small and compact.
Thunderbolt combines the PCIe and display port signals into one single port, capable of delivering data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps and high power delivery for power hungry external peripherals such as 4K monitors and portable graphics processors.
Inter-Compatibility of USB Type C and Thunderbolt
- All Thunderbolt cables will work flawlessly as USB C cables
- All USB C cables will work with Thunderbolt ports, provided they are of good quality.
- Even though the USB C cables will work with Thunderbolt ports, the functions and the speed will be limited.
- Thunderbolt 3 is backwards compatible with Thunderbolt 1 and 2 protocols, but require a compatible adapter for plugging in the cable.
Vulnerability to Hacking
Since the Thunderbolt port has access to the low-level PCIe bus, it is vulnerable to Direct Memory Access (DMA) hacks.
An attacker, in theory, can connect a specially modified malicious device to the Thunderbolt port for unrestricted access to the system memory.
Comparison Between USB Type C and Thunderbolt 3
| USB Type-C | Thunderbolt 3 |
| Data transfer speed up to 10Gbps | Data transfer speeds up to 40Gbps |
| Power supply up to 100mW | Power supply up to 100mW |
| Can connect a single external 4K display | Can connect up to two external 4k displays |
| Limited support for other protocols | Extensive support for multiple protocols |
Advantages of USB Type-C Over its Predecessors
- USB Type-C offers data transfer speeds up to 10Gbps compared to the 5Gbps speed of USB 3.0.
- The smaller size and compact form factor allow manufacturers to further reduce the size of the gadgets to make them slim and lightweight.
- USB type C comes with a maximum power supply of 100mW, that makes it compatible for hooking up power hungry peripherals to your desktop computer or laptop.
- In case of charging, the increased power supply capability allows the device to implement quick charge feature without any restrictions.
- One of the main physical advantages of USB Type-C port is that it doesn’t have any particular orientation for plugging in the port. Thank god, now you can connect it in one single try.
USB Type-C Adoption on Phones and Laptops
USB Type-C has almost become a common occurrence in laptops across the budget spectrum.
We get to see even budget laptops priced under Rs.30,000 with USB Type-C ports from OEMs such as Lenovo and Asus.
When it comes to smartphones, almost all the flagship phones come with USB Type-C connectors. Majority of the mid-rangers too have the same but the story is different with budget devices.
Most of the smartphones priced under Rs.20,000 comes with the outdated micro USB port except for a few devices such as Nokia 6.1 and the Mi A2.
It’s a shame that OEMs still prefer to bundle all the cutting edge technologies on their devices and omit the USB C from the party.
Final Thoughts
USB Type-C is the best iteration of the USB connectivity till date and is definitely here to stay.
The faster-charging speeds and data transfer rates give this connector and the underlying implementation a definite edge over micro USB and other USB types.
Having the maximum current carrying capacity of up to 100 mW allows the USB C to be used with a variety of external peripherals ranging from simple USB pen drives to a full-fledged 4K display.
With the technology catching up fast and the prices coming down, we can expect that almost all gadgets will have USB C by default replacing the legacy USB and micro USB ports in a few years.
